Introduction to programming, with Python and Jupyter#
About this course#
Websites
French version of the course: Website
English version of the course: Website (temporary) Open in JupyterLite Open in mydocker
Educational objectives
This course, currently under construction, offers an introduction to programming, using the Python programming language and the Jupyter interactive environment. It is composed of a collection of interactive sheets that allow you to discover, independently and in successive steps, the basic concepts of programming.
Prerequisites
The course aims to have no prerequisites other than familiarity with the use of the internet and the web; simply follow the instructions. Some sheets or exercises – identified as such and non-essential – assume a familiarity with high school mathematics.
How to use this course
Renater Education Research Federation (staff and students of all French higher education institutions)
Connect to the serviceMyDocker@Paris-Saclay:- click «connection via renater federation»;
choose your institution (tip: type for example “Sacl” to find Université Paris-Saclay) and enter your credentials;
click «request an environment»;
click «connection to the interface» for «Download the course …».
Follow the instructions on the home page (which will be similar to this document).
Outside the Renater Education Research Federation
You can work on the educational materialonline with JupyterLite. Limitation: your work will be saved in your web browser. If you change computers or web browsers, you will not find it. The version deployed above is also a bit old.
Alternatively, you can download the educational material fromhere(Code -> Download source code -> zip). You will also need to install a certain number of software (jupyterlab, jupylates, Laby).
Installation instructions with conda
If you don’t already have it, install the environment managerconda. We recommend using theMiniforge installer.
If you don’t already have it, install
mamba(faster thanconda; provided directly by miniforge) :conda install -c conda-forge mamba
Download the environment description :
git clone https://gitlab.dsi.universite-paris-saclay.fr/mydocker/images/jupyter-python
Install the required software :
cd jupyter-pythonmamba env create
Activate your conda environment :
conda jupyter-python
Install the configuration files :
cp -r install-files/\* \$CONDA_PREFIX
To open the documents, launch JupyterLab from the folder containing them :
jupyter lab
Attention
To access the provided software, you will need to repeat step 5 of activation each time you open a new terminal.
A free and reusable course
![]()
This shared course is intended to become a common foundation of reusable sheets for various introductory programming courses, at Saclay or elsewhere. It can also be used independently.
In the spirit of digital commons, this course incorporates or is inspired by numerous existing educational resources, at the Faculty of Orsay (Info 111: Introduction to programming, in C++, etc.) and elsewhere (Laby, Introduction to Programming in Python for Biology by P. Fuchs and N. Poulain). These elements will be cited as they appear (🚧under construction🚧).
This course itself is under CC-BY-SA license (Creative Commons, Attribution, Share under the same conditions): you are encouraged to reuse any element and distribute derivative products, provided that you share it under the same conditions and attribute the original work to the authors. A collaboration with CodEx is under consideration. This course also relies on many free software.
This course is also a showcase and an experimentation ground for teaching with Jupyter. See the writing conventions. Coming soon: description of pedagogical strategies, tools used: MyST, Jupylates, etc.
This project is supported since 2024 by SaclAI-School and is part of the larger project py-edu-fr since its launch in 2025.
Educational Path#
Note
You can adapt the educational path proposed here according to your experience. You can also explore the table of contents, where the sheets are classified by theme. You will notice that the proposed path rotates among the themes, returning to them in turn to deepen them (spiral learning).
0 - Discover Jupyter#
In this course, you will use Jupyter interactive worksheets.
Jupyter is a web application that allows you to program interactively in many languages
(Python, C++, …), a bit like a super calculator, and to
write interactive documents.
Indication
If you are already familiar with using Jupyter, you can skip directly
to the next section.
Open the worksheet00-PriseEnMainJupyter.md.
Follow the instructions it contains.
1 - Discover Python#
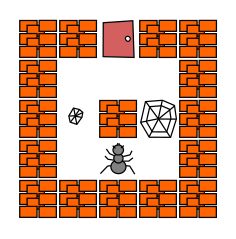
The Laby game offers several successive challenges; for each of them, the goal is to guide an ant step-by-step towards the exit of a labyrinth using a program. Each of these challenges will be an opportunity to have a first playful contact with some concepts (program, conditionals, loops, functions) that we will explore in more depth later.
Learn more about Laby
The game Laby was originally created by Stéphane Gimenez and collaborators for the Science Festival at Jussieu. We will use here a
Notes to teachers
Laby is not just a game. The goal is to capitalize on the notions that students will have thus perceived intuitively, such as the sequential execution of a program, loops, conditionals, functions, etc.
A common mistake is forgetting to put debut().
Each sheet below corresponds to a challenge. Open them one by one in order and follow the instructions included. If you get stuck on one of the challenges, don’t hesitate to move on and come back to it later.
Repeat:
Adapt:
Count:
2 - Calculate#
3 - Adapting to the context: conditional instructions#
4 - Repeat: Iterative instructions (loops)#
Attention
Challenges marked with a ♣ or ♣♣ are (significantly) more advanced; unless you are comfortable
and looking for a bit of a challenge, we recommend skipping them and coming back to them
later when you have seen the underlying concepts more formally.
5 - Structuring a program: functions#
6 - Structuring Data#
Todo
dictionaries / sets
tuples / immutability
7 - Communication: Inputs / outputs#
Todo
Print avancés
Ecrire / lire dans un fichier
lire depuis le clavier
Widgets ?
récuperer des informations depuis un site web
8 - Structuring a program: modules#
Todo
modules, packages, imports,
classes
9 - Additional challenges#
generic algorithms
